Would you like to know where your organisation stands and where the biggest opportunities for improvement lie?
The Digital Maturity Scan shows where Lean has the most impact.

Efficient. Scalable. Lean.
Many manufacturing companies lose time and resources every day due to waste, inefficient processes and a lack of overview. Not because employees are not doing their jobs properly, but because systems and structures are inadequate. Lean Manufacturing does not offer a temporary solution to this, but a strategic way of working. It enables companies to continuously improve, eliminate waste and deliver maximum value to their customers.
/Aesseal-Logo-White.png)
/Rolls-Royce-Logo-White.png)
/BAE-Systems-Logo-White.png)

Lean manufacturing is more than just a method for reducing waste. It is an organisation-wide framework in which customer value is central and continuous improvement is the standard. Not as isolated initiatives, but as part of the daily way of working, from production to purchasing, from planning to management. Lean requires a culture in which everyone takes responsibility for quality, speed and efficiency, and where every employee is given the opportunity to contribute to improvement.
In a modern, data-driven production environment, digital lean tools are indispensable for reinforcing this culture. Where traditional means such as paper improvement proposals or visual boards are finite, digital solutions offer real-time insight, direct feedback and scalable improvement processes. By integrating lean principles with systems such as MES, PLM and ERP, an adaptive organisation is created that responds more quickly to disruptions, detects deviations at an early stage and makes continuous adjustments. In this way, lean manufacturing becomes not only a way of working but also a strategic advantage.

Lean is not just about strategy, but about action. Its strength lies in practical applications that deliver visible results. Examples include Value Stream Mapping to identify waste and Kaizen to stimulate improvements directly from the shop floor. With 5S, you create a safe and well-organised working environment, while Just-in-Time and Kanban optimally align production with demand. Techniques such as SMED (Single Minute Exchange of Dies), Poka Yoke and Total Productive Maintenance also contribute: they reduce changeover times, prevent errors at source and minimise downtime.
What connects all these methods is that their effect becomes even more powerful when you combine them with digital systems. Real-time data adds speed and precision to Lean: bottlenecks are identified more quickly, adjustments can be made immediately and improvements have more impact. This not only makes Lean more efficien, it makes it smarter.

Implementing Lean starts with making sharp choices. You start by choosing one specific process where you want to see improvement. Then you determine what is truly valuable to your customer within that process. Taking this customer value as your starting point, you work through the entire process step by step. Which actions contribute to that value? Which do not?
Next, you critically analyse the process. You look for waste, where errors occur and what takes up unnecessary time. Based on these insights, you draw up a concrete improvement plan. In this plan, you specify what changes are needed, how you will implement them and who is responsible for what. Finally, you implement the improvement plan in practice. You continuously measure the results so that you know whether the changes are actually working. Only when you know what is improving and what is not can you continue to optimise.
This approach forms the core of the five principles of Lean: determining value, identifying value streams, creating flow, introducing pull and continuous improvement.
The Digital Maturity Scan shows where Lean has the most impact.
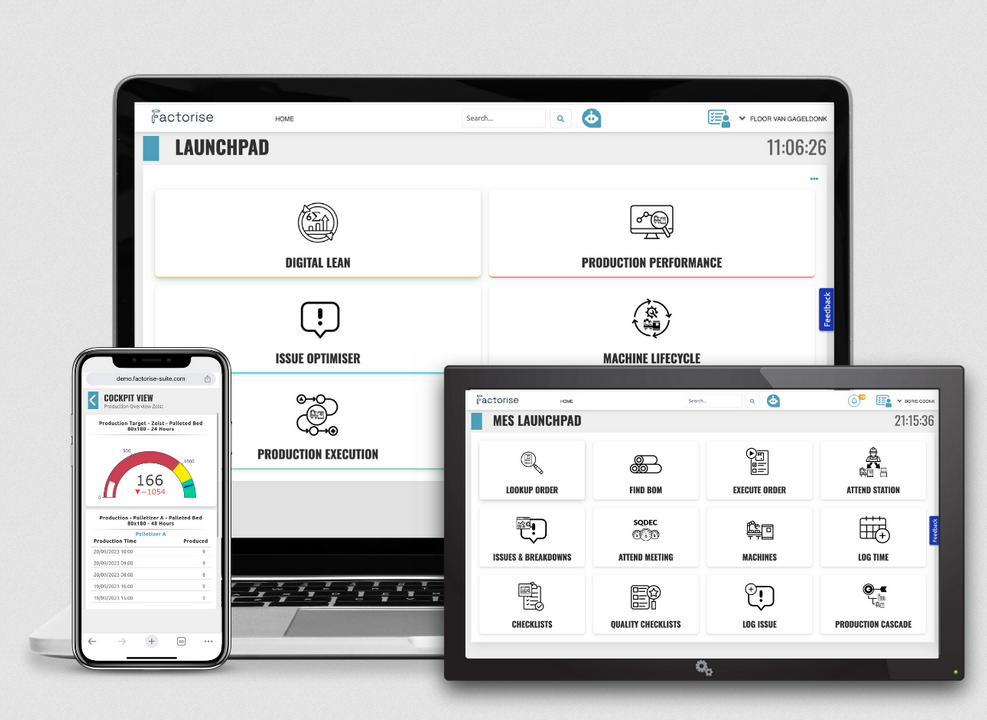
Factorise was developed as a digital accelerator for lean manufacturing. This tool helps organisations not only to visualise their production processes, but also to understand, improve and secure them. With Factorise, you can visually track the entire value stream, from raw input to end product. The system detects deviations, reveals trends and suggests concrete improvement actions. These actions are not only identified, but also followed up with structure, ownership and measurable results. Factorise translates data into action.
The power of Factorise lies in the smart lean suite it offers. Think of modules for daily gemba walks, which enable teams on the work floor to identify and address problems more quickly. Project management is fully integrated, so that improvement initiatives can be seamlessly planned, implemented and monitored. Standardisation and action management are also part of the platform, ensuring that improvements are not incidental but sustainable. It supports lean principles such as flow, standardisation and pull, and makes it possible to apply these principles structurally.
Lean manufacturing is all about creating maximum customer value with as little waste as possible. But what does that mean for your organisation? Below, you will discover how lean not only improves processes, but also motivates people and makes your company agile for the future.
Lean starts with the question: ‘What does the customer really find important?’ By focusing only on activities that actually add value, you avoid unnecessary steps and raise the bar for quality, speed and flexibility. Your processes are better aligned with what the customer wants not what has always been done. The result: an organisation that responds to customer demand and gains trust through reliability and responsiveness.
In a lean organisation, waiting time is not a given. Waiting for materials, approvals or information not only slows down delivery, it also frustrates your people and your customer. Lean helps to design processes in such a way that each step runs smoothly, without unnecessary buffers or downtime. This not only speeds up your delivery time, but also allows you to work with less stock, fewer repetitions and more stability throughout your entire chain.
Waste is everywhere often invisible. Think of overproduction, defects, overprocessing, waiting time, transport, movement, stock and untapped talent. Lean makes these eight forms of waste visible and manageable. By identifying waste and tackling it systematically, you create room for improvement. You use resources more efficiently, increase the reliability of your processes and prevent valuable time and energy from being wasted.
Lean does not work top-down, but from the inside out. It activates people on the work floor by giving them responsibility for their own process. Employees become not only executors, but problem solvers. This encourages ownership and leads to a culture in which improvement becomes self-evident. The work floor changes from a place where problems arise to a place where solutions are born.
Change is the only constant, whether it concerns customer demand, technology or regulations. Lean enables organisations to respond quickly and thoughtfully. With flexible and scalable processes, you can effortlessly adapt to new circumstances without having to rebuild everything from scratch.
Emixa guides organisations through their entire lean transformation, from strategy to implementation. As a partner in digital transformation, we combine in-depth expertise in lean with solutions in the areas of smart manufacturing, ERP, IIoT and data integration.
We believe that lean is not a one- time improvement project, but a structural way of thinking and working. With platforms such as Factorise and our strategic guidance, we lay the foundation for sustainable, future-proof growth.
Would you like to discover what lean can do for your organisation? We are happy to help you take the first step.
Lean Production is a way of working that strives to maximise value for the customer with as little waste as possible. It revolves around the continuous improvement of processes so that products and services are delivered more efficiently, faster and with higher quality.
The Lean method is a structured approach to optimising business processes. By critically examining each step in a process, waste such as waiting times, overproduction or errors are identified and reduced. The goal is to work smarter, not harder, and to continuously improve based on facts and feedback.
The five principles of Lean together form the basis for continuous improvement. It starts with determining what is truly valuable to the customer. Next, you map out the value stream to gain insight into all the steps within the process and to identify waste. Then you organise the process in such a way that a smooth, uninterrupted flow is created. With a pull system, you ensure that only what the customer needs is produced, at exactly the right time. Finally, it's all about continuous improvement: constantly evaluating, learning and optimising.
Would you like to know more about these principles? Then read our blog.
Lean Production is a way of working that strives to maximise value for the customer with as little waste as possible. It revolves around the continuous improvement of processes so that products and services are delivered more efficiently, faster and with higher quality.
The Lean method is a structured approach to optimising business processes. By critically examining each step in a process, waste such as waiting times, overproduction or errors are identified and reduced. The goal is to work smarter, not harder, and to continuously improve based on facts and feedback.
The five principles of Lean together form the basis for continuous improvement. It starts with determining what is truly valuable to the customer. Next, you map out the value stream to gain insight into all the steps within the process and to identify waste. Then you organise the process in such a way that a smooth, uninterrupted flow is created. With a pull system, you ensure that only what the customer needs is produced, at exactly the right time. Finally, it's all about continuous improvement: constantly evaluating, learning and optimising.
Would you like to know more about these principles? Then read our blog.